If you’ve ever considered downloading an Android app, you’ve likely encountered two primary sources: the Google Play Store and various websites offering direct APK file downloads. While both deliver the same end result – an installed application on your device – the journey and, crucially, the level of security they offer are vastly different. So, what are the security differences between an apk obtained from the Google Play Store versus one sourced from a website?
The core difference lies in the security measures and vetting processes in place. Downloading an apk from the Google Play Store benefits from Google’s extensive security infrastructure, designed to detect and prevent malicious software from reaching users. In contrast, obtaining an apk from a website largely bypasses these protections, placing the responsibility and the risk squarely on the user. This article will delve deep into the specific security mechanisms employed by the Play Store and highlight the inherent vulnerabilities associated with downloading APKs from less trustworthy sources. We aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of why the source of your apk file dramatically impacts your device’s security and your personal data. By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of the significant security differences and be better equipped to make informed decisions about where you obtain your Android applications.
The Google Play Store: A Fortified Ecosystem

The Google Play Store isn’t just a marketplace for apps; it’s an ecosystem with built-in security measures aimed at protecting its users. While no system is entirely foolproof, the Play Store employs multiple layers of defense that significantly reduce the risk of encountering malicious apk files.
Google Play Protect: The First Line of Defense

Google Play Protect is a comprehensive suite of security features that actively works to keep your device and data safe. It scans apps before, during, and after installation, regardless of where they were sourced (though its effectiveness is naturally higher for apps distributed through the Play Store). Understanding its functions is key to appreciating the security differences.
H4: Malware Scanning Before Distribution
Before an apk file is even made available on the Google Play Store, it undergoes a rigorous analysis by Google’s automated systems. These scans look for known malware signatures, suspicious code patterns, and potential vulnerabilities. Apps that fail these initial security checks are typically rejected and never made available to users. This pre-emptive scanning acts as a crucial filter, preventing many malicious apk files from entering the ecosystem in the first place.
H4: Continuous Monitoring of Installed Apps
Play Protect doesn’t stop after you’ve installed an app from the Play Store. It continuously monitors the behavior of apps on your device, looking for signs of malicious activity. If an app starts exhibiting suspicious behavior, such as attempting to access data it shouldn’t or communicating with known command-and-control servers used by cybercriminals, Play Protect can warn you and even automatically remove the app. This ongoing vigilance provides an additional layer of security that is absent when installing an apk from a website.
H4: Harmful App Removals
If a malicious app somehow manages to slip through the initial checks and is later discovered by Google, Play Protect can remotely remove it from affected devices. This capability is a significant security difference. Users who have sideloaded an apk from a website do not benefit from this automatic safety net and must rely on their own vigilance and security software to identify and remove threats.
Developer Vetting and Accountability

While not a foolproof guarantee, the Google Play Store has a system in place for vetting developers. Developers are required to register and adhere to Google’s policies. This process, while it can be circumvented by malicious actors, provides a degree of accountability that is often lacking when downloading an apk from an anonymous website. If a developer is found to be distributing malware, Google can ban their account, preventing them from further distributing harmful apps through the platform.
User Feedback and Reporting Mechanisms

The Google Play Store incorporates user feedback in its security efforts. Users can report apps they suspect of being malicious or violating the store’s policies. These reports are investigated by Google, and if an app is found to be harmful, it can be removed. This community-driven aspect contributes to a safer environment compared to the often unmoderated landscape of websites offering direct apk downloads. The ability for users to collectively identify and flag potentially dangerous apk files adds another layer to the security differences.
Websites Offering APKs: Navigating a Minefield

Downloading an apk file from a website is akin to venturing into the digital wild west. While some reputable websites offer legitimate APKs (e.g., for beta testing or apps not available in the Play Store), the vast majority lack the security measures and oversight of the Google Play Store, creating a breeding ground for malware. Understanding these risks is paramount when considering the security differences.
Lack of Centralized Security Scanning

Unlike the Play Store, websites offering direct apk downloads typically do not have robust, automated security scanning processes in place. The apk file you download could be clean, or it could be riddled with malware – there’s often no way to be sure before you install it. You are essentially trusting the website operator’s integrity and security practices, which can vary wildly and are often non-existent. This lack of pre-download scanning is a critical security difference.
Anonymity and Lack of Developer Accountability

Websites offering APKs often provide little to no information about the app’s developer. This anonymity makes it difficult to verify the legitimacy of the app and holds no one accountable if the apk contains malware. In contrast, the Google Play Store requires developers to provide contact information, adding a layer of transparency and accountability. When you download an apk from an unknown website, you have no recourse if the app turns out to be malicious.
Higher Risk of Tampered or Modified APKs

One of the significant dangers of downloading an apk from a website is the increased likelihood of encountering tampered or modified apps. Cybercriminals often take legitimate apps and inject them with malware before distributing them on third-party websites. These modified apk files can look and function like the original app but secretly steal your data in the background. The Play Store’s integrity checks make it much harder for such tampered apps to be distributed. The potential for encountering malicious modifications highlights a key security difference.
Limited User Feedback and No Centralized Reporting

Unlike the Google Play Store, most websites offering APKs lack a robust system for user feedback and reporting. If you download a malicious apk from a website, there’s often no easy way to warn other users or report the issue to a central authority. This lack of community-driven security leaves users more vulnerable.
Exposure to Drive-by Downloads and Malicious Ads

Websites offering APKs, especially those of dubious reputation, often employ aggressive advertising tactics, including pop-ups, redirects, and even drive-by downloads. A drive-by download can occur without your explicit consent, where a malicious apk file or other malware is downloaded to your device simply by visiting the website. This risk is significantly lower when using the Google Play Store.
Specific Security Risks Associated with Website APKs

To further illustrate the security differences, let’s delve into some specific types of threats you are more likely to encounter when downloading APKs from websites.
H3: Banking Trojans and Financial Malware
Cybercriminals frequently disguise banking Trojans as legitimate-looking apps on third-party websites. Once installed, these malicious apk files can steal your banking credentials, intercept SMS-based two-factor authentication codes, and even overlay fake login screens on top of legitimate banking apps to harvest your information.
H3: Spyware and Data Theft
Spyware embedded in an apk downloaded from a website can silently collect a wide range of your personal data, including call logs, SMS messages, contacts, browsing history, location data, photos, and videos. This information is then surreptitiously transmitted to the attacker.
H3: Ransomware
While less common, some malicious apk files found on websites can deploy ransomware, encrypting your device’s data and demanding a ransom payment for its release.
H3: Fake and Cloned Apps
Attackers often create fake versions of popular apps or clone legitimate apps and inject malware into them. These malicious apk files are then distributed on third-party websites, tricking users into downloading them.
H3: Adware and PUPs (Potentially Unwanted Programs)
Even if an apk from a website doesn’t contain outright malware, it might be bundled with aggressive adware that floods your device with unwanted advertisements, drains your battery, and consumes your data. Potentially Unwanted Programs (PUPs) can also be included, which might change your browser settings or collect usage data without your consent.
Mitigating Risks When Sideloading (If Absolutely Necessary)
While the safest approach is to stick to the Google Play Store, there might be rare instances where you need to sideload an apk from a website (e.g., for legitimate beta testing from a trusted developer). In such cases, it’s crucial to take extra precautions to minimize the security risks and acknowledge the inherent security differences.
H3: Verify the Source and Developer
If you must download an apk from a website, ensure the website is reputable and uses HTTPS. If possible, verify the identity of the developer and cross-reference the app with information available on their official website or other trusted sources.
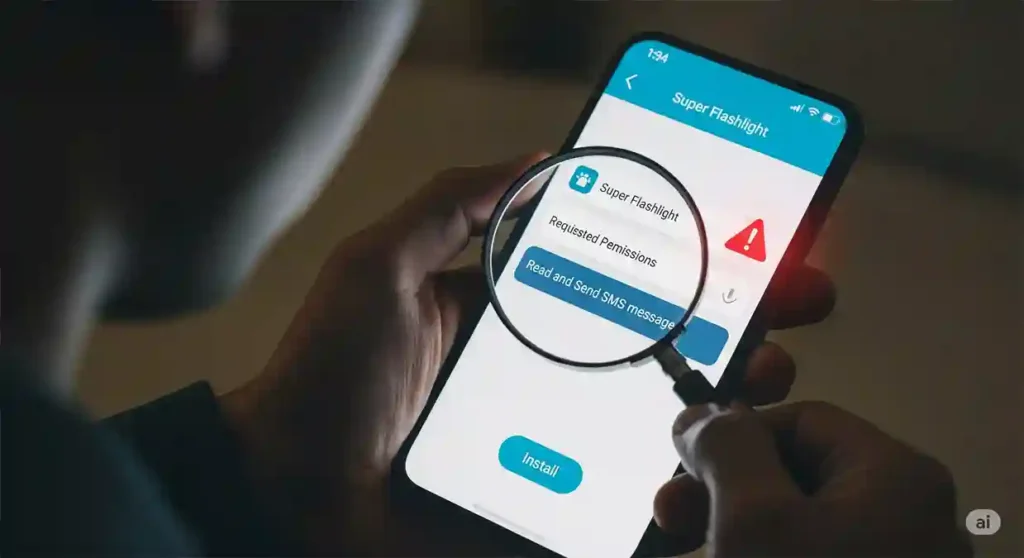
H3: Check App Permissions Before Installation
Before installing any apk, carefully review the permissions it requests. Be suspicious of apps that ask for permissions that seem irrelevant to their functionality. For example, a simple utility app shouldn’t need access to your contacts or SMS messages.
H3: Use a Reputable Mobile Security App
Install a robust mobile security app from a well-known vendor and scan the apk file before you install it. This can help detect known malware. Regularly run full scans of your device as well.
H3: Keep Your Android OS Updated
Ensure your Android operating system is up to date with the latest security patches. Malware often exploits known vulnerabilities in older versions of the OS.
H3: Be Wary of Third-Party App Stores
While some alternative app stores might have better security than random websites, they generally do not offer the same level of protection as the Google Play Store. Exercise caution when using them.
H3: Consider Using a Sandbox Environment (Advanced Users)
Advanced users might consider using a sandbox environment on their device to test the apk in an isolated space before installing it on their main system.
The Clear Winner in Security: The Google Play Store

When it comes to the security differences between obtaining an apk from the Google Play Store versus a website, the Play Store is the clear winner. Its multi-layered security measures, including pre-upload scanning, continuous monitoring with Play Protect, developer vetting, and user feedback mechanisms, provide a significantly safer environment for downloading and installing Android applications. While no system is perfect, the Play Store dramatically reduces the risk of encountering malicious apk files compared to the often unvetted and potentially dangerous landscape of websites offering direct downloads. Choosing the Play Store for your app downloads is a fundamental step in protecting your device and your personal information.
Have you ever had a security scare after downloading an app from a source other than the Play Store? Share your experiences and any lessons you learned in the comments below! If you found this article insightful, please consider sharing it with your friends and family to help them stay safe online.






